Subtotal $0.00
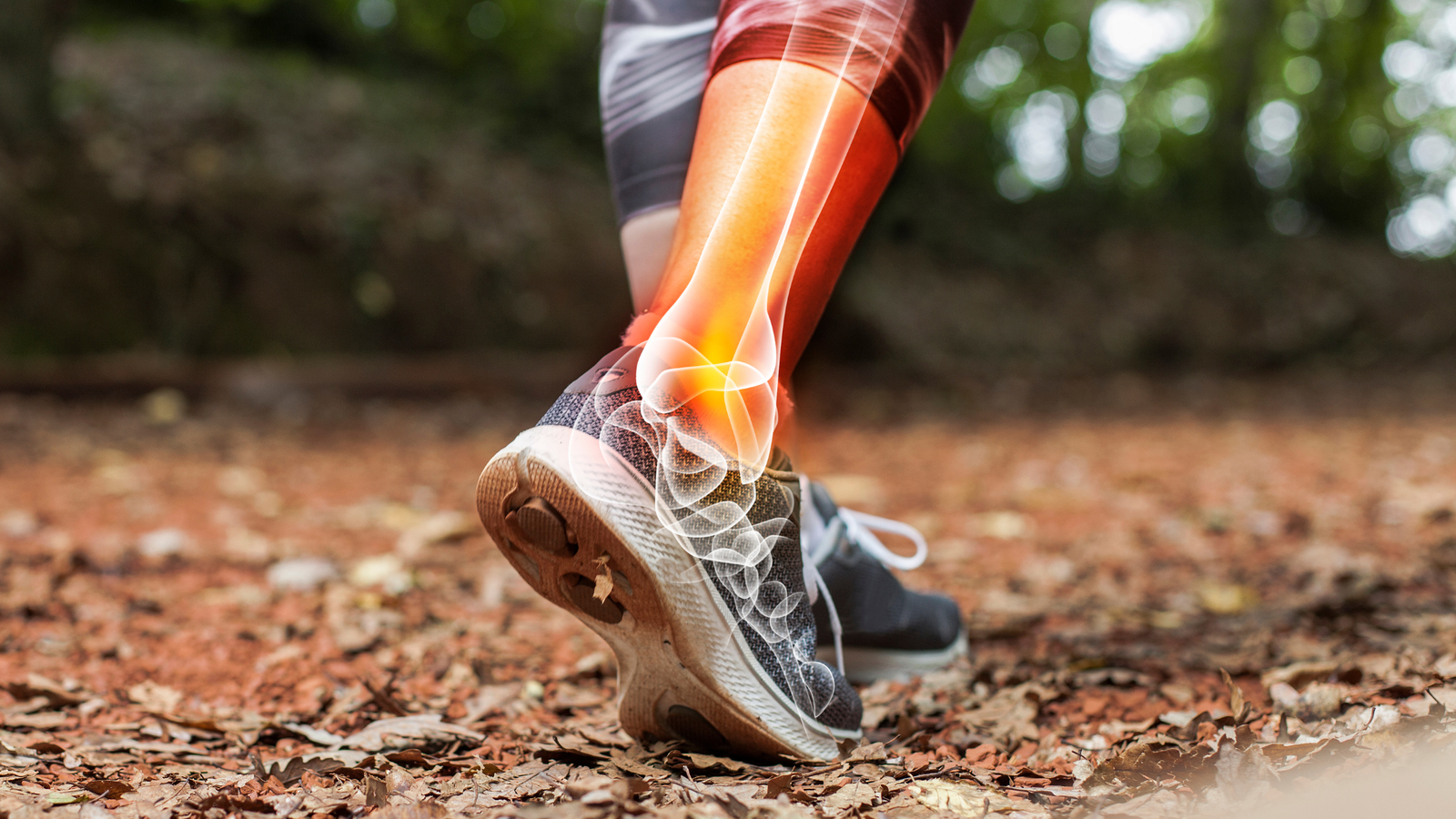
Orthopedic injuries are among the most common types of injuries affecting individuals across all age groups. From athletes and active individuals to older adults, these injuries can significantly impact one’s quality of life, causing pain, limited mobility, and even long-term disability if not properly treated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for common orthopedic injuries is crucial for prevention and effective management.
Dr. Subhash Jangid, one of the best orthopedic doctors in India, shares his expert insights on how to manage these injuries effectively.
1. Sprains and Strains
Sprains and strains are some of the most frequent orthopedic injuries. A sprain occurs when the ligaments, the tissues that connect bones to one another, are stretched or torn. Strains, on the other hand, involve the muscles or tendons, which connect muscles to bones.
Causes:
- Sudden twists or falls
- Overstretching during physical activity
- Lifting heavy objects improperly
- Poor conditioning or lack of warm-up before exercise
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness
- Swelling and bruising
- Limited range of motion
- Muscle spasms (in case of strains)
Treatment:
- R.I.C.E. Method: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation are the first line of treatment.
- Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening and flexibility exercises.
- In severe cases: Surgery may be required to repair torn ligaments or tendons.
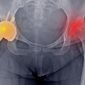
2. Fractures
A fracture refers to a break in the bone, which can range from a small crack to a complete break. Fractures are classified into different types, including simple (closed), compound (open), stress, and comminuted fractures.
Causes:
- Trauma from accidents falls, or sports injuries
- Osteoporosis, a condition that weakens bones
- Overuse or repetitive stress, especially in athletes
Symptoms:
- Severe pain at the injury site
- Swelling and bruising
- Deformity (in cases of displaced fractures)
- Inability to move the affected limb
Treatment:
- Immobilization: Using a cast, splint, or brace to keep the bone in place as it heals.
- Medication: Pain relief and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Surgery: In cases of severe fractures, surgical intervention with metal plates, screws, or rods may be necessary.
- Rehabilitation: Physical therapy to restore strength and mobility after the bone heals.
3. Dislocations
A dislocation occurs when the bones in a joint are forced out of their normal positions. This injury often happens in the shoulder, knee, elbow, or fingers.
Causes:
- Trauma from falls or blows
- Sports injuries
- Sudden impact or collision
- Overstretching the joint
Symptoms:
- Intense pain
- Swelling and bruising
- Visible deformity of the joint
- Inability to move the affected joint
Treatment:
- Reduction: A medical professional will manipulate the joint back into its normal position.
- Immobilization: The joint is kept still with a sling, splint, or cast to allow healing.
- Pain Management: NSAIDs or prescription painkillers may be prescribed.
- Physical Therapy: To strengthen the muscles around the joint and prevent future dislocations.
- Surgery: May be needed if the dislocation damages surrounding tissues.
4. Tendonitis
Tendonitis is the inflammation of a tendon, often caused by repetitive motion or overuse. Common types include Achilles tendonitis, tennis elbow, and golfer’s elbow.
Causes:
- Repetitive motion in sports or occupational activities
- Sudden increase in physical activity
- Poor technique in sports or exercise
- Aging, as tendons lose elasticity over time
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness along the tendon
- Swelling and warmth in the affected area
- Stiffness, especially in the morning
- Difficulty moving the affected joint
Treatment:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the condition.
- Ice Therapy: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and pain.
- Medication: NSAIDs to reduce inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen and stretch the tendon.
- Corticosteroid Injections: To reduce severe inflammation.
- Surgery: Rarely needed, but may be considered if conservative treatments fail.
5. Rotator Cuff Injuries
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that stabilize the shoulder. Injuries to the rotator cuff can range from inflammation (tendinitis) to partial or complete tears.
Causes:
- Repetitive overhead motions, often seen in athletes and laborers
- Degeneration of the tendon due to aging
- Acute trauma from falls or accidents
Symptoms:
- Dull ache deep in the shoulder
- Weakness in the arm
- Difficulty raising the arm above the head
- Pain that worsens at night or with specific movements
Treatment:
- Rest and Ice: To reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to improve flexibility and strength.
- Medication: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Steroid Injections: For severe inflammation.
- Surgery: In cases of complete tears, surgery may be required to reattach the tendon.
6. Bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of the bursae, small fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons, and muscles near joints. This condition commonly affects the shoulder, elbow, hip, and knee.
Causes:
- Repetitive motion or prolonged pressure on a joint
- Trauma or injury to a joint
- Infection
- Underlying conditions like rheumatoid arthritis
Symptoms:
- Pain and tenderness around the affected joint
- Swelling and redness
- Limited range of motion
- Pain that worsens with movement or pressure
Treatment:
- Rest: Avoid activities that exacerbate the pain.
- Ice Application: To reduce swelling and pain.
- Medication: NSAIDs to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises to strengthen muscles around the joint.
- Aspiration: Removal of excess fluid from the bursae.
- Surgery: In rare cases, removal of the inflamed bursa may be necessary.
Conclusion
Orthopedic injuries can range from mild sprains and strains to more severe fractures and dislocations. Understanding the causes and symptoms of these injuries is essential for proper prevention and treatment. Early intervention, guided by an experienced orthopedic doctor in India like Dr. Subhash Jangid, can help ensure a full recovery and prevent long-term complications.
Whether you’re an athlete, an active individual, or someone recovering from an injury, consulting with a specialist ensures that you receive the best care tailored to your specific needs. Remember, timely treatment not only relieves pain but also restores your mobility and quality of life.